Continuing with a series of clean energy resources, we’ve known about Solar Power Plant Construction in our previous article. This time, learn about Wind farm Power Plant Construction.
Wind energy offers many advantages, which explains why it’s one of the fastest-growing energy sources in the world. Research efforts are aimed at addressing the challenges to greater use of wind energy. Read on to learn more about the benefits of wind power and some of the challenges it is working to overcome. So what is Wind farm power plant construction?
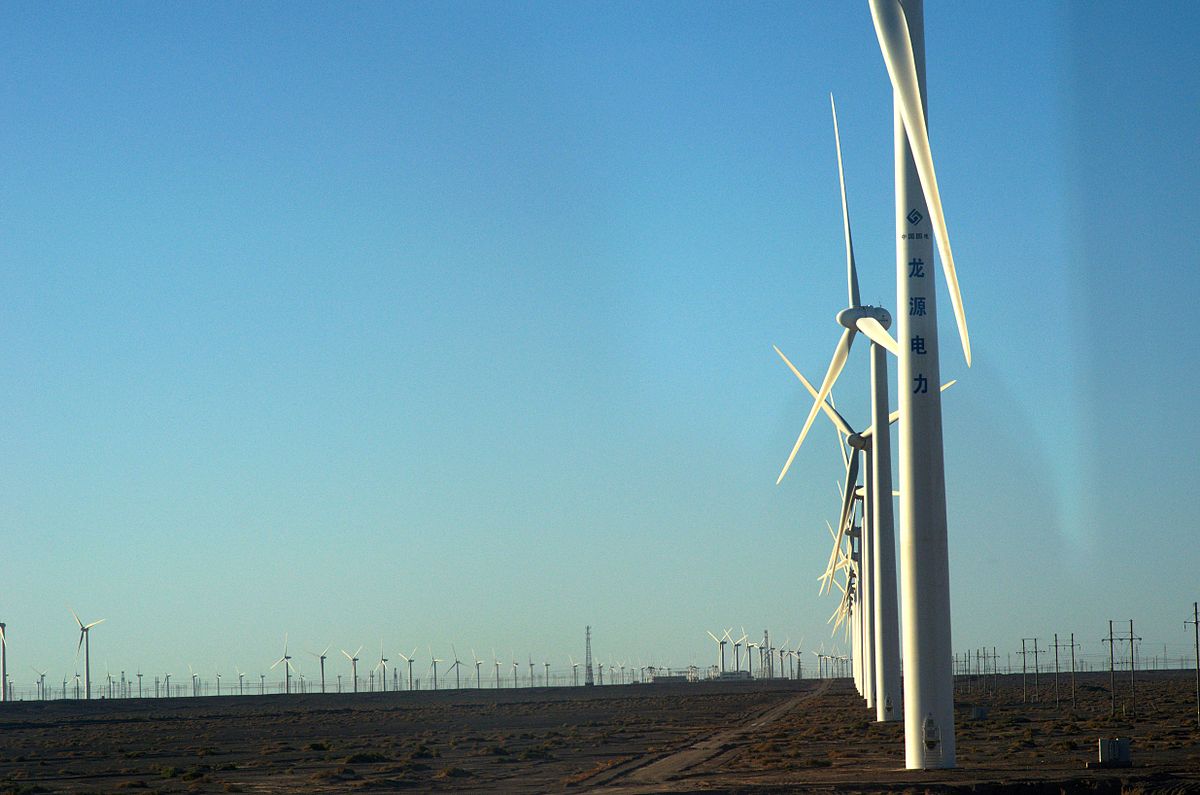
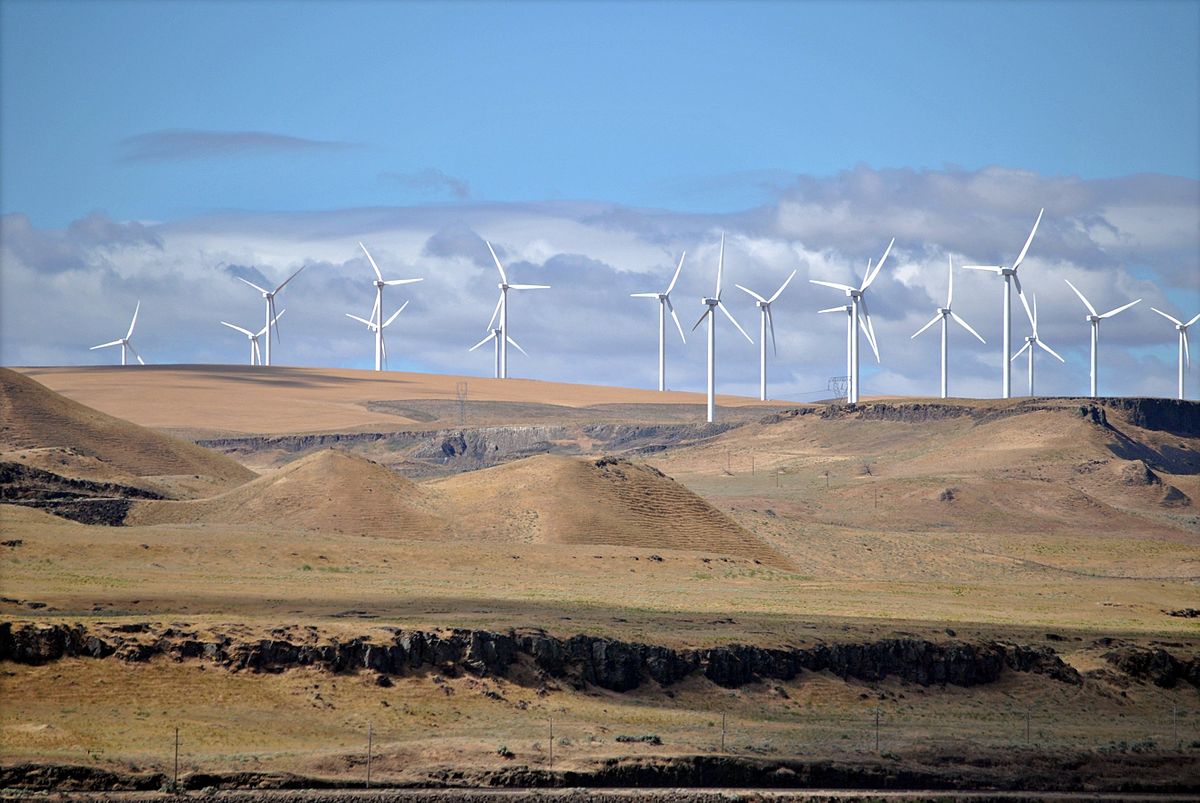
A wind farm power plant construction is a group of wind turbines in the same location used for production of electric power. A large wind farm may consist of several hundred individual wind turbines distributed over an extended area, but the land between the turbines may be used for agricultural or other purposes. For example, Gansu Wind Farm, the largest wind farm in the world, has several thousand turbines. A wind farm may also be located offshore.
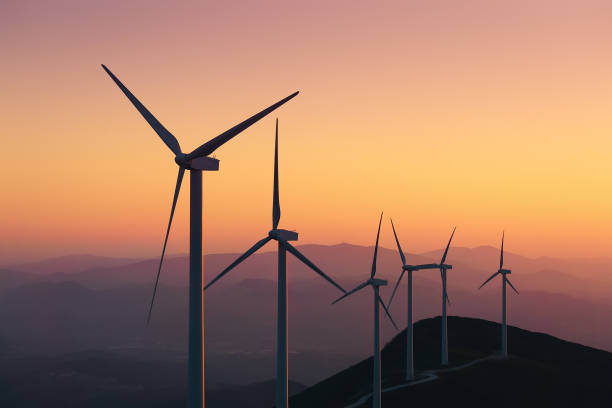

Almost all large wind turbines have the same design — a horizontal axis wind turbine having an upwind rotor with three blades, attached to a nacelle on top of a tall tubular tower.
In a wind farm, individual turbines are interconnected with a medium voltage (often 34.5 kV), power collection system and communications network. In general, a distance of 7D (7 × Rotor Diameter of the Wind Turbine) is set between each turbine in a fully developed wind farm. At a substation, this medium-voltage electric current is increased in voltage with a transformer for connection to the high voltage electric power transmission system.
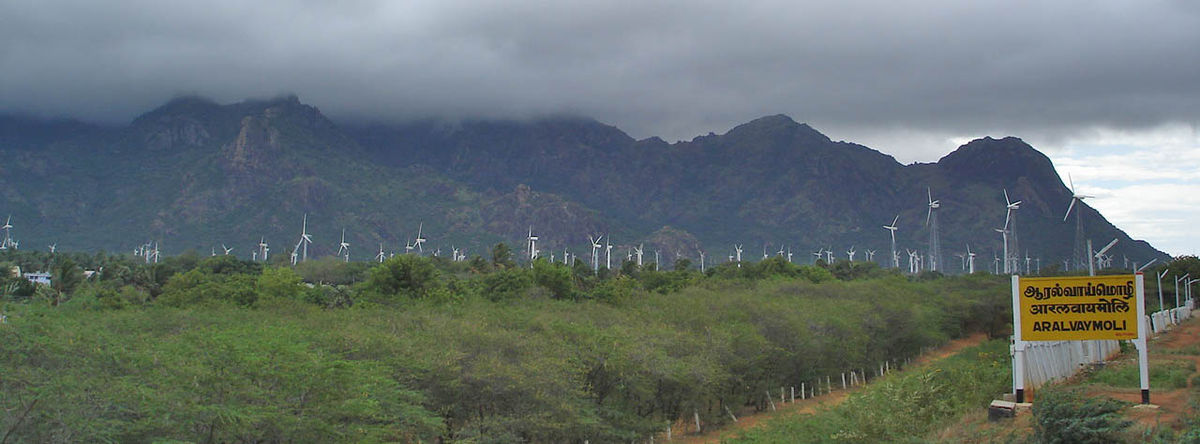
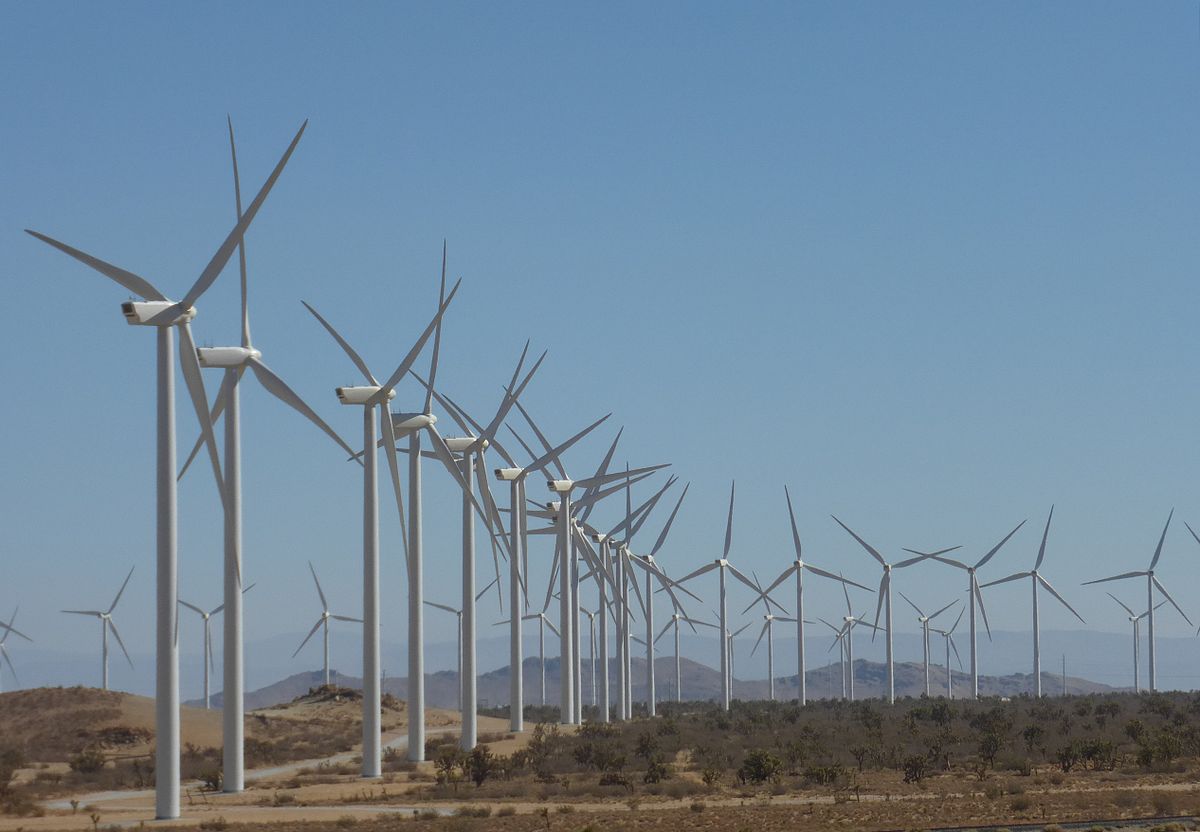
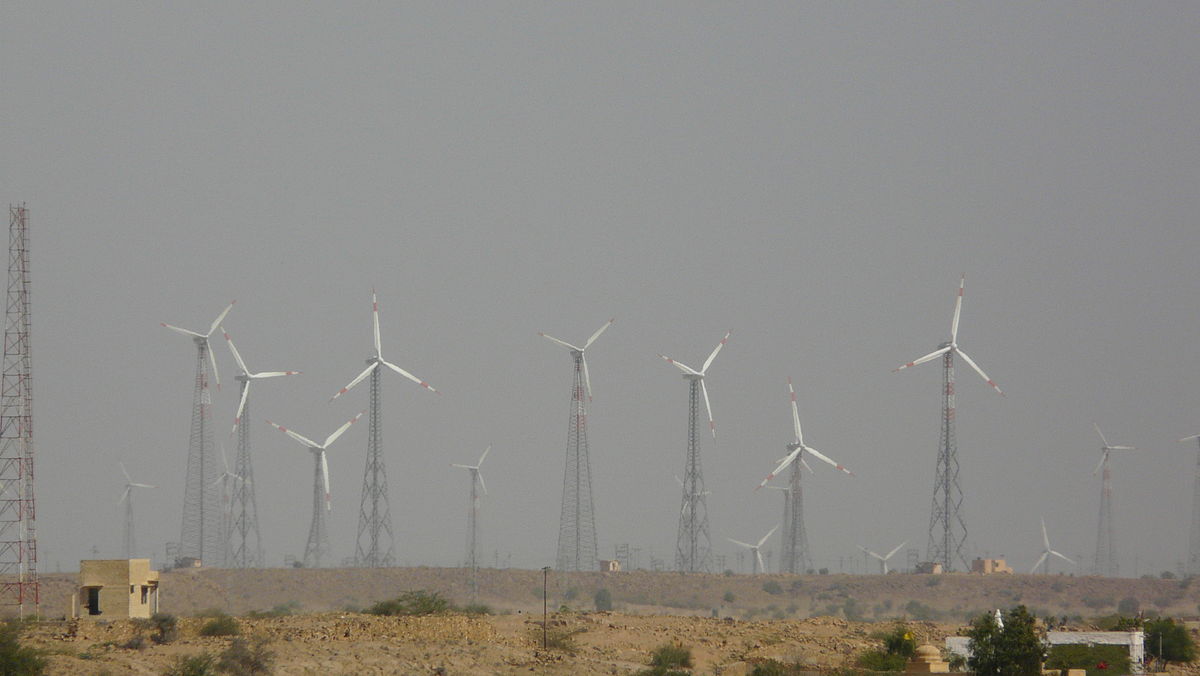
Large onshore wind farms (Source: Wikipedia)
Wind energy is one of the fastest growing sources of new electricity generation in the world today. These growth trends can be linked to the multi-dimensional benefits associated with wind energy.
Why we should use Wind power?
The Dutch famously adapted enhancements of the windmill and used it to drain lakes and marshes in the Rhine River Delta. In the late 19th century, this technology was brought to the New World by settlers who then pumped water to farms and ranches and later generated electricity for homes and industry. In Europe and later in America, industrialization led a steady decline in the use of windmills. However, it also sparked the development of larger windmills in order to generate electricity. These windmills became known as wind turbines which appeared in Denmark as early as 1890.

Electric power was fed to the local utility network for months during WWII by the largest wind turbine known in the 1940′s. This wind turbine sat on a Vermont Hilltop known as Grandpa’s Knob and was rated at 1.25 megawatts in winds of about 30 mph.
Popularity of wind energy usage has always fluctuated with the price of fossil fuels. Interest in wind turbines waned after World War II when fuel prices fell. But by the 1970s, when price of oil escalated, the interest in wind turbine generators rose proportionately.
For many years to come, the fastest growing energy source of wind energy will power industry, business and homes with clean renewable electricity.
Advantages and Challenges of Wind Energy
Advantages
Challenges
Wind power is cost-effective
Wind creates jobs
It's a clean fuel source.
Wind is a domestic source of energy.
It's sustainable.
Wind turbines can be built on existing farms or ranches.
Good wind sites are often located in remote locations.
Wind resource development might not be the most profitable use of the land.
Turbines might cause noise and aesthetic pollution.
Turbine blades could damage local wildlife.
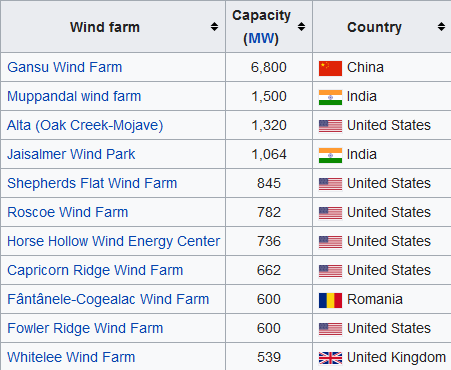
Largest operational onshore wind farms (based on capacity)
CONTACT INFO:
Address: 400/3 Ung Van Khiem Street, Binh Thanh District, Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam Tel: (+84) 28 66 56 54 54 / (+84) 28 73 00 76 78 Fax: (+84)8 73 00 20 07 Email: info@khangducconst.com













